Bucket sort is a sorting algorithm also knows as bin sort,
it works with distributing elements of an array into a number of buckets.
A bucket is most commonly a type of data buffer or a type of
document in which data is divided into regions. Elements or contents in the
bucket are unsorted and size of the bucket is fixed at the time of creation.
A bucket has states of empty, non-empty, full or partly
full, and overflows.
Each bucket is sorted individually, using any sorting
algorithm or bucket sorting. Basically
bucket sort is distribution sort and it is cousin of radix sort. Bucket sort
can be implemented with comparisons and therefore can also be considered a
comparison sort algorithm.
Worst – case performance: O(n2)
Best Case Performance:
Ω(n+k)
Average Performance:
θ(n+k)
Worst case space complexity: O(n.k)
Pseudo code of Bucket sort:
function
bucketSort(array, n) is
buckets ← new array of n empty lists
for i = 0 to (length(array)-1) do
insert array[i] into
buckets[msbits(array[i], k)]
for i = 0 to n - 1 do
nextSort(buckets[i]);
return the concatenation of
buckets[0], ...., buckets[n-1]
Please look at the instance:
Given Series is: [34,12,45,23,1,3,4,36,19,20,28,56,67,48,59]
Distribute these elements into buckets/bins like below
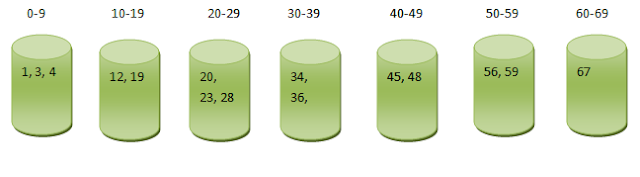 |
| Distribution of given Elements in Buckets |
In the above picture elements are distributed among the
bins/buckets
 |
| Sorting in Each Bin |
Elements are sorted in each bin/bucket.
Implement bucket sort in java:
import java.util.*;
public class BucketSort{
public static void
sort(int[] a, int limit) {
int [] bucket=new
int[limit+1];
for (int i=0;
i<bucket.length; i++) {
bucket[i]=0;
}
for (int i=0;
i<a.length; i++) {
bucket[a[i]]++;
}
int outPos=0;
for (int i=0;
i<bucket.length; i++) {
for (int j=0;
j<bucket[i]; j++) {
a[outPos++]=i;
}
}
}
public static void
main(String[] args) {
int limit=5;
int [] data=
{5,3,0,2,4,1,0,5,2,3,1,4};
System.out.println("Before: " + Arrays.toString(data));
sort(data,limit);
System.out.println("After:
" + Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
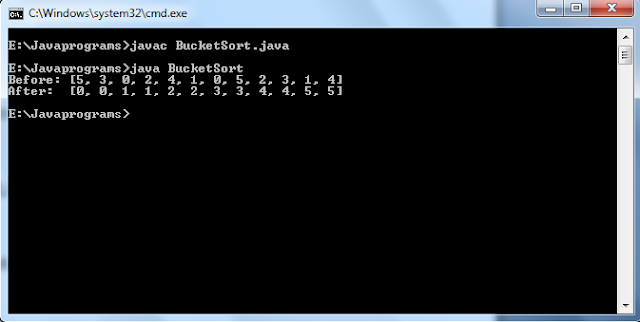
Out put of the above program is: