Merge Sort is a sorting technique based on divide and conquer
technique with comparison.
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows :
i) Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list
of 1 element is considered sorted).
ii) Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sublists until there is only 1
sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
 |
| Merge sort - Visualization |
Worst Case performance: O (n log n)
Best case Performance: O (n log n) for typical O(n) natural
variant
Average performance: O(n log n)
Worst case space complexity : O(n)
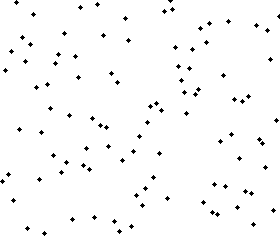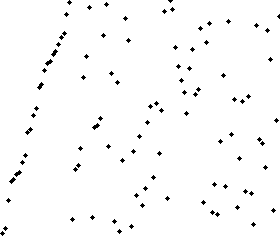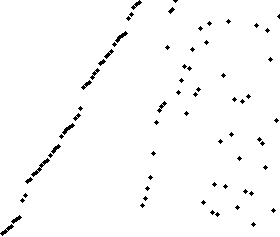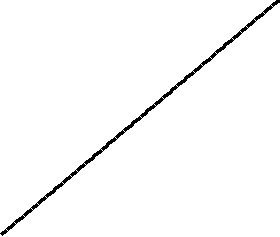 |
| Merge Sort |
Merge Sort Pseudocode and Algorithm:
MergeSort
(Array(First..Last))
Begin
If Array contains only one element Then
Return Array
Else
Middle= ((Last + First)/2) rounded
down to the nearest integer
LeftHalfArray =
MergeSort(Array(First..Middle))
RightHalfArray =
MergeSort(Array(Middle+1..Last))
ResultArray = Merge(LeftHalfArray,
RightHalfArray)
Return ResultArray
EndIf
End MergeSort
Java Program for Merge Sort:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MergeSort
{
public static void sort(int[] a, int low, int high)
{
int N = high - low;
if (N <= 1)
return;
int mid = low + N / 2;
sort(a, low, mid);
sort(a, mid, high);
int[] temp = new int[N];
int i = low, j = mid;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
if (i == mid)
temp[k] = a[j++];
else if (j == high)
temp[k] = a[i++];
else if (a[j] < a[i])
temp[k] = a[j++];
else
temp[k] = a[i++];
}
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
a[low + k] = temp[k];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Merge Sort Test\n");
int n, i;
System.out.println("Enter number of integer elements");
n = scan.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[n];
System.out.println("\nEnter " + n + " integer elements");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = scan.nextInt();
sort(arr, 0, n);
System.out.println("\nElements after sorting ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
Output :
Tags
Computer Science
